On This Page:
What do the examiners look for?
- Accurate and detailed knowledge
- Clear, coherent, and focused answers
- Effective use of terminology (use the “technical terms”)
In application questions, examiners look for “effective application to the scenario,” which means that you need to describe the theory and explain the scenario using the theory making the links between the two very clear.
If there is more than one individual in the scenario, you must mention all of the characters to get to the top band.
Difference between AS and A level answers
The descriptions follow the same criteria; however, you have to use the issues and debates effectively in your answers. “Effectively” means that it needs to be clearly linked and explained in the context of the answer.
Read the model answers to get a clearer idea of what is needed.
Exam Advice:
You MUST revise everything – because the exam board could choose any question. However, it does make sense to spend more time on those topics which have not appeared for a while.
Exam Tip:
With these particular questions, there is a sizeable risk that people don’t understand the difference between the questions and then write about the wrong thing.
Make sure you know which is which; for example, do you understand the difference between “Genetic explanations” and “Neural and hormonal explanations,” and do you have a model essay for each?
Problems in Defining Crime
AO1
• Deviance involves breaking society’s norms and values
• Crime involves breaking a law
AO3
What is considered a crime and how that act is dealt with varies considerably from culture to culture?
Almost all research in forensic psychology can be considered ethnocentric as it is only relevant to the culture where the research was carried out.
For example, bigamy is illegal in the UK but not in all cultures. The age of criminal responsibility is 10 in England & Wales, but 8 in Scotland (being raised to 12) and 14 in most other European countries.
Definitions of crime change over time. For example, a parent’s right to smack their own child was outlawed in 2004. Homosexuality became legal in Britain in 1967.
A02 Scenario Question
In the UK, it is against the law to have more than one wife or husband at the same time. Smacking children was not illegal before 2004 in the UK, but now it can be a criminal offense.
1) Referring to the statements above, explain two problems in defining crime. [4 marks]
Answer
It is difficult to define crime because definitions of crime are culturally specific. Whilst it is illegal to practice polygamy in the UK, it is not illegal in some other countries.
A further issue is that definitions of crime change over time, for example, it was perfectly legal to smack your child in the UK before 2004, but now it is against the law, and public attitudes and perceptions have also changed.
Ways of Measuring Crime: Official Statistics
AO1
• Official Statistics are government records of all recorded crime in the previous year, based on police reports. They are published by the Home Office annually.
AO3
Official statistics lack validity as not all crime is reported or recorded by the police. For example, domestic violence against men is an under-reported crime.
They may also lack reliability as there are differences between police forces about which crimes are recorded, for example, some police forces do not record theft if the value is less than £10.
Also, they only count the number of criminal acts rather than the number of criminals, so the overall picture might be misleading. It could be that relatively few criminals are responsible for the majority of crime in an area.
Ways of Measuring Crime: Victim Surveys
AO1
Victim Surveys such as the Crime Survey for England and Wales selects 50,000 households randomly and asks them to document any crimes they have been a victim of in the past year.
AO3
Respondents may get years mixed up and report a crime happening in that year when in fact, it was the year before. This is known as telescoping.
Furthermore, some people may be unaware that they have been a victim of crime, e.g., thefts of garden sheds may only be discovered months later or assumed that the item is misplaced, not stolen.
However, victim surveys could be higher in validity than official statistics as victims are more likely to report trivial offenses in these surveys, things they wouldn’t go to the police with, as they might think it a waste of time.
Ways of Measuring Crime: Offender Surveys
AO1
• Offender Surveys involve Individuals volunteering the number and types of crimes they have committed.
• These tend to target groups of likely offenders based on ‘risk’ factors such as previous convictions, age, social background, etc.
• The Offender Crime and Justice Survey was the first self-report survey of its kind in England and Wales.
AO3
These obviously lack validity as offenders are unlikely to be truthful about the real extent of their own criminality. It may also be that they can’t accurately remember how many crimes they have committed and exactly when they took place.
All methods to measure crime are hampered by what is known as the dark figure of crime. As all the methods used to measure crime have issues with reliability and validity, a better approach might be to take a multidisciplinary approach and combine all three methods to get the best possible picture of the extent of crime in England & Wales in any year.
General Criticisms of Measuring Crime
AO3
Essay Question
Describe & evaluate ways of measuring crime. Refer to evidence and/or published examples in your answer (16 Marks)
Plan (16 marks – 20 minutes – 400-500 words)
- A01: – Official Statistics
- A03: – Police don’t record all crimes (Why?)
- All crimes are not reported (Why?)
- A01: – Victim Surveys
- A03: – Issues with memory (was it this year!) Victims might not report a crime (Why?)
- A01: – Offender Surveys
- A03: – Validity, social desirability, demand characteristics. Why wouldn’t offenders tell the truth?
- Conclusion: – Dark figure of crime. True picture through triangulation of all ways of measuring crime
Offender Profiling
When police have very little evidence to go on, they will sometimes enlist the help of a forensic psychologist.
The forensic psychologist will use prior knowledge, and evidence gathered from the scene to build an offender profile.
An offender profile outlines the type of person likely to have committed the crime. It is based on prior experiences and uses computer databases to analyze what is already known. Offender profiles are only as good as the information provided to the profiler.
They should be regarded as one tool amongst many to be used by the police.
Top Down – The FBI Approach
AO1
• The phrase top-down refers to an approach that starts with the big picture and then fills in the details. The Top Down FBI approach relies on previous experiences of crimes.
• In the 1970s, the FBIs Behavioral Science Unit gathered data from 36 sexually motivated serial killers, including Charles Manson & Ted Bundy, to develop this approach to Offender Profiling.
• In 1980, Hazelwood and Douglas published their account of the ‘lust murderer.’ They advanced a theory that lust murderers are mainly categorized into two types: – Organised and disorganized. This is an example of a top-down typology.
• An organized offender leads an ordered life and kills after some sort of critical life event. Their actions are premeditated and planned, they are likely to bring weapons and restraints to the scene. They are likely to be of average to high intelligence and employed.
• A disorganized offender is more likely to have committed the crime in a moment of passion. There will be no evidence of premeditation, and they are more likely to leave evidence, such as blood, semen, murder weapon, etc., behind. This type of offender is thought to be less socially competent and more likely to be unemployed.
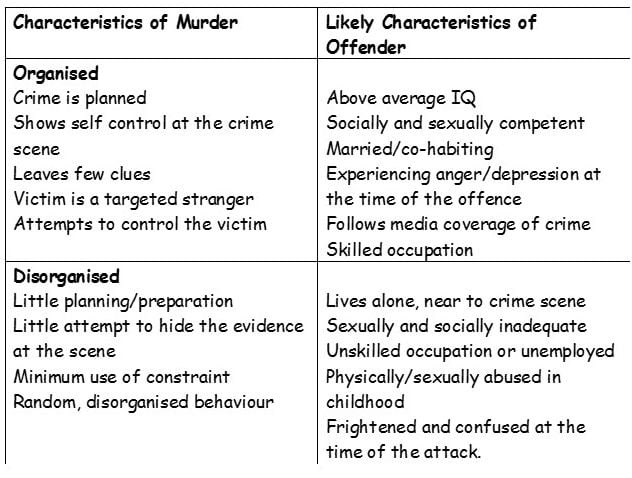
AO3
Top-down profiling is reductionist, as the classification system (organized/disorganized) is too simple. Offenders are not simply either disorganized or organized. It may be that there are both organized and disorganized features to all their crimes. An offender may start off being disorganized and become more organized as they develop their modus operandi.
Top Down typology can only be applied to sexually motivated serial killers; because of the limitations of the original sample that they interviewed: – sexually motivated serial killers!).
Alison et al. (2002) argue that this approach is based on outdated theories of personality being stable. External, situational factors can be a major influence on offending, and they are constantly changing.
Bottom-up – The British Approach
AO1
• A bottom-up approach that starts with small details and creates the big picture. No initial assumptions are made about the offender, and the approach relies heavily on computer databases. It can be the little details that are often overlooked that can be crucial to the success of a case.
• Canter (1990) is the UK’s foremost profiling expert; his bottom-up approach looks for consistencies in offenders’ behavior during the crime. Canter’s most famous case is that of the ‘Railway Rapist’ John Duffy.
• John Duffy carried out 24 sexual attacks and 3 murders of women near railway stations in North London in the 1980s. David Canter analyzed the geographical details and the evidence and drew up a surprisingly accurate profile. However, it should be noted that the profile didn’t directly lead to John Duffy’s arrest.
AO3
Bottom-up has wider applications; it can be applied to other crimes, not just sexually motivated serial killers like top-down.
Profiles can be useful, but police must be careful not to be blinded to other possibilities by them. Occasionally criminals do not fit the profile. Overuse could lead to miscarriages of justice. E.g., Paul Britton’s misleading profile in the hunt for the killer of Rachel Nickell.
Investigative Psychology
AO1
• Using computer databases and a program called Smallest Space Analysis, patterns are identified, and it is possible to see if a series of offenses are linked.
• Central to this approach is the concept of interpersonal coherence. This means the behavior of the offender at the time of the crime will be comparable to what they’re like in everyday life. Degrees of violence used in serious crimes, especially rape, may reflect how the criminal treats other women in his non-criminal life.
AO3
Evidence supports investigative psychology. Canter & Heritage (1990) analyzed 66 sexual assault cases using Smallest Space Analysis and identified clear common patterns of behavior.
The use of computer databases and Smallest Space Analysis makes this approach much more scientific than top-down typologies.
Geographical Profiling
AO1
• Geographical Profiling is used to make inferences about where an offender is likely to live. This is also known as crime mapping.
• Canter’s Circle theory (1993) proposed two models of offender behavior. Offenders are classified as either marauders (who commit crimes close to home) or commuters (who travel away from home to offend).
• It is called circle theory as most offenders (marauders) do operate in an area they are familiar with, and their crimes form a circle around their usual residence.
• It is more difficult to geographically profile commuters, although when investigators were looking at the disappearance and murder of 4 young girls from different and seemingly unrelated areas of Britain in the 1980s, the dumping of the bodies in laybys next to major A roads (including Twycross, just up the road) led to a breakthrough. It was realized that his likely occupation was delivery driver, giving him access to a van/lorry for easy transportation and leading to him ‘commuting’ all over the country, traveling along A roads.
AO3
Evidence supports geographical profiling. Lundrigan & Canter (2001) collated evidence from 120 murder cases and found that the offender’s home base was invariably located in the center of the crime scene pattern.
Essay Questions
Discuss the top-down approach to offender profiling. Refer to evidence in your answer (16 marks).
Discuss the bottom-up approach to offender profiling. Refer to evidence in your answer (16 marks)
Discuss investigative psychology and/or geographical offender profiling. Refer to evidence in your answer (16 marks)
Biological explanations of crime
Atavistic Form
AO1
• Lombroso’s (1876) theory of Criminology suggests that criminality is inherited and that someone “born criminal” could be identified by the way they look.
• He suggested that there was a distinct biological class of people that were prone to criminality. These people exhibited ‘atavistic’ (i.e., primitive) features.
• Lombroso suggested that they were ‘throwbacks’ who had biological characteristics from an earlier stage of human development that manifested as a tendency to commit crimes. Lombroso claimed that criminal types were distinguishable from the general population because they looked different.
• In a study of 383 dead Italian criminals and 3839 living ones, he found 40% of them had atavistic characteristics.
• These features include: – large jaw, forward projection of jaw, low sloping foreheads, high cheekbones, flattened or upturned nose, handle-shaped ears, large chins, very prominent in appearance, hawk-like noses or fleshy lips, hard shifty eyes, scanty beard or baldness, insensitivity to pain, long arms and tattoos!
AO3
These early theories seem ridiculous to us now, but they did represent the beginning of offender profiling and modern forensic science. Lombroso did also champion the use of the scientific method by using an evidence-based approach to research, doing hundreds of observations and measurements.
However, Lombroso did not have a control group of non-criminals, so it could just have been that those characteristics are common in the general population.
Lombroso has been accused of scientific racism; some of the characteristics he identified are more prevalent in certain racial groups.
However, this is still an issue today. Eberhardt found that stereotypically ‘black’ looking men were much more likely to get the death penalty in the USA than those who were less stereotypically black looking, even if they had committed very similar offenses!
The physical differences Lombroso discovered were much more likely to be the result of other factors such as poverty, poor diet, illness, and disease.
Goring (1913) did find evidence that criminals tended to have lower-than-average intelligence. But, this may mean crime is due to a lack of education rather than any biological factors.
Lombroso’s theory lacks temporal validity. It is a child of its time when eugenic theories were very popular.
Neural Explanations of Offending behavior
AO1
• Adrian Raine of the University of Southern California has conducted research using PET scanning and found abnormalities in some parts of the brain in violent criminals.
• Most of the criminals in these studies have been diagnosed with Antisocial Personality Disorder (APD). Raine has discovered that these individuals have reduced activity in the prefrontal cortex of the brain, the part of the brain that regulates emotional behavior. Put simply, they find it difficult to control their impulses and do not suffer from guilt or remorse.
• Raine studied 41 violent offenders and compared the activity in their prefrontal cortex to 41 non-criminals (including six schizophrenics) using PET scans. The violent offenders showed significantly less activity in the prefrontal lobe than the other participants suggesting less control over impulsive behavior.
• The prefrontal lobe develops relatively late, sometimes not fully developed until the early 20s and later in males. This may explain the peak in antisocial behavior by male teenagers!
AO3
Not every criminal has APD or an abnormal brain structure. These theories can only explain a small minority of extreme cases. Everybody has free will. We choose whether or not to break the law.
+ Use of scientific method and scientific equipment, e.g., PET scans.
Explaining crime simply through brain structure is very reductionist. Crime is complex, and the reasons for people turning to crime are many and varied.
A good example of these criticisms is the case of Jim Fallon: – Professor of Psychiatry at the University of California, Irvine. Jim Fallon has the brain of a serial killer – Low activity prefrontal cortex and the defective version of the MAOA gene.
BUT he is not a serial killer! Something he attributes to his fabulous childhood and supportive family. A case of nurture triumphing over nature.
Genetic explanations of Offender behavior
AO1
- Price (1966) suggested that males with an extra Y chromosome XYY ‘supermale’ were predisposed towards violent crime. Individuals with XYY are above-average height and below-average intelligence. It might be the latter characteristic (Low intelligence) that accounts for their over-representation in prison populations.
- Christiansen (1977) looked at 3586 twin pairs in Denmark. A 52% concordance rate for criminality was found for monozygotic (identical) twins, compared to just 22% for dizygotic (non-identical) twins.
- However, we must remember the effects of shared upbringing, and if crime really was genetic, we would expect a 100% concordance rate for monozygotic twins as they share 100% of their genes.
- Brunner studied a genetic abnormality commonly known as the ‘warrior gene’ as it is associated with excessively violent and aggressive behavior, which may lead to crime. This mutation/abnormality on the X chromosome leads to increased levels of MAOA. As MAOA removes the neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, and noradrenaline, this leads to lower levels of these neurotransmitters, which can then lead to behavioral problems.
- Reduced levels of dopamine and noradrenaline cause problems with inappropriate violent and sexual behavior. The impaired metabolism of serotonin is also likely to be responsible for mental issues, and this could be linked to aggressive behavior.
AO3
There is support for the diathesis-stress model of crime. Someone may have biological tendencies towards crime, but they will need some sort of environmental trigger in order to actually become a criminal. (Nature and Nurture)
We must avoid biological determinism; genes are not destiny. Criminals have free will.
Explaining crime simply through genes is very reductionist. Crime is complex, and the reasons for people turning to crime are many and varied.
A good example of these criticisms is the case of Jim Fallon: – Professor of Psychiatry at the University of California, Irvine. Jim Fallon has the brain of a serial killer – Low activity prefrontal cortex and the defective version of the MAOA gene.
BUT he is not a serial killer! Something he attributes to his fabulous childhood and supportive family. A case of nurture triumphing over nature.
Essay Questions
Discuss the atavistic form as an explanation for criminal behavior. Refer to evidence in your answer (16 marks).
Discuss genetic and/or neural explanations of offending. Refer to evidence in your answer (16 marks)
Psychological Explanations of Crime
The central idea of this topic is that for aggression to be an adaptive feature, it has to serve a purpose.
Eysenck’s Theory of Personality
AO1
• According to Eysenck, our personality is innate and has a biological basis. There is a personality type known as the criminal personality. Individuals with a criminal personality will score highly on measures of extraversion, neuroticism, and psychoticism.
• These people are seen as difficult to condition (train) and cold and unfeeling, and it is these traits which may explain their criminality.
AO3
Evidence to support this theory comes from Eysenck’s study of 2070 male prisoners and 2422 male controls. The prisoners scored higher on extraversion, neuroticism, and psychoticism than the non-criminal controls.
However, Farrington reviewed several studies and only found evidence of prisoners scoring higher on measures of psychoticism.
The idea of one personality type explaining all offending behavior is not very plausible; there are many different types of both crimes and offenders. All criminals are not the same.
This research can be seen as culturally biased. Holanchock studied Black and Hispanic criminals in America and found them to be less extroverted than non-criminal control groups.
The validity of measuring personality through a psychometric test is also questionable, as is the notion that personality is a stable entity. Most people would argue that personality changes over the years and as a person matures.
Eysenck’s theory is similar to other biological explanations of offending, such as Anti-social personality disorder (APD). However, whilst Raine explains this through neural differences, Eysenck attributes it to the functioning of the nervous system.
Therefore, although Eysenck’s theory is seen as a psychological theory as it focuses on personality, it could also be accused of biological determinism as it sees personality as innate and unchanging.
Cognitive Explanations – Cognitive Distortions
Please see article on Kohlberg’s theory of moral development.
Differential Association Hypothesis
AO1
• This explanation for offending suggests that through interaction with others, individuals learn the values, attitudes, techniques, and motivation for criminal behavior.
• We often hear the phrase “Got in with a bad crowd”; our friendship groups can profoundly affect criminality, especially during adolescence.
• Differential associations (number of contacts with criminals over non-criminals) may vary in frequency, duration, priority, and intensity.
• The process of learning criminal behavior by association with criminal and anti-criminal patterns involves all of the mechanisms that are involved in any other learning. (behaviorism: classical conditioning, operant conditioning, social learning theory).
• The principal part of the learning of criminal behavior occurs within intimate personal groups.
AO3
This theory does not account for individual differences. Some people are much more susceptible (easily led) to the influence of others. Therefore the theory neglects to consider the role of temperament and personality.
This theory shifted the emphasis away from biology and eugenics arguments for criminality.
It can also account for white-collar crime, and indeed it was Sutherland who coined the term. Differential association can explain crime for all races, gender, and social groups.
This theory is impossible to test. How do you count up someone’s associations and influences accurately?
– Farrington found that the family is a large influence on offending. Crime can be seen as inter-generational.
Psychodynamic Theories
AO1
- The psychodynamic explanation of offending behavior sees the Superego, the moral component of the personality, as crucial in explaining criminality.
- Blackburn (1993) argues that if the superego (the moral part of the personality) is deficient, then criminality is inevitable as the Id (pleasure principle) is not properly controlled, and we are going to give in to our urges and impulses.
- Weak Superego may develop if the same-sex parent is absent during the phallic stage of psycho-sexual development. This would mean that we would fail to internalize the moral values of same-sex parents.
- Deviant Superego may develop if the child internalizes the morals of a criminal or deviant same-sex parent.
- Overharsh Superego may develop if the same-sex parent is overly harsh. This may mean an individual is crippled by guilt and anxiety and commits a crime in order to satisfy the superego’s need for punishment.
- • Another psychodynamic theory is Bowlby’s maternal deprivation hypothesis. This predicts that if an infant is deprived of a mother or mother figure during the critical period of attachment in the first few years, then there will be serious and permanent consequences. These consequences included mental abnormalities, delinquency, depression, affectionless psychopathology, and even dwarfism!
AO3
However, this theory has been heavily criticized. Freud’s theory is seen as sexist as he focuses on the Oedipus Complex and adds the Electra complex as an afterthought.
In fact, Freud argued that females were less moral than males. This is because males fear castration by their fathers for moral transgressions, whereas females only fear losing their mother’s love!
However, the vast majority of criminals are male, not female. Males outnumber females in prisons throughout the world.
There is little evidence to back up this theory, many children grow up without a same-sex parent, and the vast majority do not turn to crime. Although family influence is undeniably a factor in criminality, individuals with delinquent parents or siblings are much more likely to turn to crime.
The idea of the over-harsh superego and wanting to be punished does not stand up to scrutiny; most criminals go to great lengths not to be caught and punished!
Essay Questions
Discuss Eysenck’s theory of the criminal personality. Refer to evidence in your answer (16 marks).
Describe and discuss cognitive explanations of offending. Refer to at least one other explanation of offending in your answer (16 marks)
Discuss the differential association theory of offending. Refer to at least one other explanation of offending in your answer (16 marks)
Discuss two or more psychodynamic explanations of offending. Refer to evidence in your answer (16 marks)
Dealing with Offender behavior
In 2016 the UK prison population was 86,000, despite having an official capacity of only 78,000, leading to serious overcrowding. (Howard League).
What are the implications of this?
In order for the prison to work, prisoners must be educated and made more employable to ensure they are more likely to remain out of prison and instead contribute to society. Otherwise, prisons become simply ‘Universities of crime.’
Research has shown (Prison Reform Trust 2007) that many prisoners have not reached the levels of literacy and numeracy expected of an average 11-year-old; 50% in writing, 66% in numeracy, and 80% in reading. 50% do not have the skills required by 96% of all jobs, and 50% have been excluded from school.
These statistics make prisoners, along with their criminal records, virtually unemployable without successful educational intervention within the prison system.
Many people are critical of the parole system (the fact that prisoners are often released early and rarely serve their full sentence); however, this is an important incentive crucial to the smooth operation of the prison system. Applications for parole are allowed after a minimum term (set by the judge) has been served.
Success will depend on the nature of the offense, the judge’s comments on sentencing, and, crucially, the inmate’s behavior in prison. This gives the prisoner an incentive to behave and comply with prison rules. Without this incentive, many inmates would be unmanageable.
Aims of Custodial Sentencing and its Effects
AO1
Aims of Custodial Sentencing
1) Deterrence – Prison should be an unpleasant experience. So someone who serves a prison sentence should never wish to serve another. The thought of prison should act as a deterrent to others and prevent them from committing crimes.
2) Incapacitation – Taking a criminal out of circulation means they are unable to commit further crimes, keeping society safe.
3) Retribution – Society is taking revenge on the criminal. They are paying for their crimes by having their freedom taken from them.
4) Rehabilitation – Prison can be used to reform criminals through training, education, and therapy so they leave prison a changed person.
Psychological Effects of Custodial Sentencing
1) Stress and Depression – Suicide rates are higher in prison than in the general population, as are cases of self-harm. If a prisoner suffers from mental health issues before their sentence, this is likely to worsen in prison.
2) Institutionalisation – Having adapted to the norms and values of prison life, some prisoners find it impossible to cope in the real world on their release. Some even commit crimes with the intention of being arrested and returned back to the comfort of what they know – prison.
3) Prisonisation – Similar to institutionalization, some behaviors that are unacceptable in the outside world are encouraged and rewarded inside the walls of a prison. Prisoners learn to accept the prisoner code in order to survive, for example, the unofficial hierarchy of prisoners.
AO3
The study you learned about last year is useful here. Zimbardo’s main conclusions were that situational factors were more useful for explaining the behavior of prisoners and guards than individual ones. Zimbardo’s participants conformed to their ideas of how prisoners and guards should behave.
Prisons are very regimented, and prisoners have to conform to strict rules and regulations. They are told when to sleep, wake, eat, exercise, etc. They have no autonomy. The problem arises when prisoners have served long sentences and become very accustomed to the prison way of life. This means they find it very hard to adapt to life on the outside.
In order to combat the problems of institutionalization and prisonisation, prisoners need to be well prepared for their release. This might mean a move to an open prison or lessons in life skills. Without these skills, they will be unable to cope and will soon find themselves back in prison.
Curt Bartol (1995) has suggested that prison is ‘brutal, demeaning and generally devastating.’ Suicide rates are generally 15 times higher than in society in general. Most at risk are young, single men in the first 24 hours of incarceration. Around 25% of female and 15% of male prisoners have symptoms of psychosis (severe mental illness)
Individual differences – Not all prisoners react in the same way to incarceration. Some punishment should fit the individual, not necessarily the crime!
Rehabilitation – Cuts to prison budgets mean that education, training, and therapy are not always available or effectively delivered. So opportunities for rehabilitation are limited.
University of Crime – Putting young, inexperienced criminals into a prison environment with older, more experienced criminals may mean that the type of education these youngsters get is not necessarily the type we would want!
Recidivism
AO1
• The aim of prison is to punish and rehabilitate offenders in the hope that they will not re-offend. Re-offending is known as recidivism. The prison has a poor record for reducing reoffending – 57% of offenders will re-offend within a year of release (2013).
• Over two-thirds (67%) of under 18-year-olds are reconvicted within a year of release offending by all recent ex-prisoners in 2007-08 cost the economy between £9.5 and £13 billion.
AO3
In order to reduce recidivism (i.e., re-offending), punishment needs to fit the individual as well as the crime and more research is needed into reducing the negative psychological effects of imprisonment.
The aim should be for offenders to leave prison fully reformed and ready to take on the role of productive and law-abiding citizens.
Alternatives to imprisonment – Given that we know prison doesn’t work, we need alternatives. Some alternatives include probation and restorative justice.
However, the government is reluctant to invest in prisoners due to economic restraints and public opinion. But, this is a short-sighted approach; in order to cut crime and recidivism rates, investment is needed (Economic implication).
Behavior Modification
AO1
• Therapies based on the principles of operant conditioning aim to bring about specific changes in behavior. This is known as behavior modification. It involves rewarding ‘appropriate’ behavior and withholding rewards for ‘inappropriate’ behavior.
• This approach usually works best with children or in institutions such as mental hospitals, schools, and prisons. For example, children can be observed and supervised by parents and teachers working with therapists. As a result, their behavior can be consistently and systematically reinforced.
• Token economies illustrate the application of operant conditioning principles to adults in institutional settings. They were introduced into mental hospitals in the USA in the 1960s. Tokens, such as plastic discs, are given as rewards for ‘desirable’ behavior. The tokens can then be exchanged for privileges. In theory, tokens reinforce ‘appropriate’ behavior. House credits are used in the same way in schools.
• Hobbs and Holt (1976) introduced a token economy program with young delinquents in three behavioral units, and a fourth acted as a control. They observed a significant improvement in a positive behavior as a result of the introduction of the token economy. Allyon (1979) found similar effects in an adult prison.
AO3
Token economies are easy to implement and do not require specialist training or expense, like other therapies such as Anger Management. But, all staff must implement them consistently if they are to work.
The effects they appear to produce may not be primarily due to the token economy. Patients may be responding to increased attention, a planned system of activities, and improved monitoring rather than a desire to get tokens.
Token economies may not really change behavior – people may simply mimic or fake ‘desirable’ behavior in order to get tokens. On release, prisoners revert back to previous criminal behaviors.
Token economies raise ethical issues. Is it ethical to withhold ‘privileges’ such as watching TV because a severely disordered person does not do what a nurse thinks is desirable? Are people’s human rights threatened when staff can control their access to food and their freedom of movement?
Clinton Field (2004) found that for maximum effect, the rewards and frequency of them needed to be individually tailored to the inmate. Think about house credits; whilst they work well with Year 7 students, a school mug or pen is hardly going to motivate a Year 11 student!
Anger Management
AO1
• Anger Management programs are a form of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT); they aim to change the way a prisoner thinks and, therefore the way they act.
• There are three stages in Anger Management: –
1) Cognitive Preparation: – The offender is encouraged to reflect on their past behaviors and what makes them angry. The therapist works with them to show them that their response is irrational and helps them to redefine the situations as non-threatening. They are taught to recognize their own triggers for anger.
2) Skill Acquisition: – The offenders are taught a range of techniques and skills to enable them to avoid triggers and deal with anger-provoking situations more rationally. They might require training in assertiveness and effective communication. They are taught how to control their own emotions rather than being ruled by them.
3) Application practice: – Offenders practice their new skills through role-play. The therapist will deliberately provoke them to see how they react. The therapist will positively reinforce successful strategies.
• Ireland (2000) Investigation of whether anger management courses work. A natural experiment compared a group of 50 prisoners who had completed CALM and a group of 37 who were assessed as suitable but had not actually taken the course. Prisoners who had completed CALM rated themselves lower on the anger questionnaire and were rated lower by the prison officers than the control group. 92% showed improvements on at least one measure of aggression and anger. Conclusions: – In the short term, the treatment seemed effective, but there is no re-offending data.
AO3
Anger management is an eclectic approach. It uses a cognitive approach in stage 1, a behavioral in stage 2, and a social in stage 3. This recognizes that offending behavior is the complex interaction between social and psychological factors.
Anger management is more likely to lead to a permanent change in behavior than behavior modification programs (token economies), as it focuses on changing the way an offender both thinks and behaves.
Although Anger Management works in the short term, the lack of re-offending data means we don’t know if the effects last. It is very different from role-playing controlling anger to controlling anger once outside of prison.
Anger management is limited in its application as not all crime is motivated by anger. Crimes for financial gain, for example, would not benefit from any form of CBT, as they are logical!
Anger Management is very expensive and time-consuming as it requires highly skilled therapists. Also, the prisoner must be motivated and want to change. (How many Psychiatrists does it take to change a light bulb? One – but the light bulb must really want to change!)
Restorative Justice Programmes
AO1
• Restorative justice usually involves a supervised mediation meeting between the victim and the offender with a trained mediator. The victim is given the opportunity to confront the offender and explain the impact the crime has had on their life. The offender has to face up to the consequences of their actions, and this starts the rehabilitation process.
• Restorative justice has to be voluntary for all parties and seeks a positive outcome. It is respectful and not degrading for either offender or victim.
Aims of Restorative Justice
• Rehabilitation of Offenders – Being punished is a passive process; restorative justice requires the offender to be an active participant in the process. It is tough for the offender they have to listen to the impact of their crimes on the victim and take full responsibility for their actions. The experience should reduce the likelihood of them reoffending.
• Atonement for Wrongdoing – Offenders may offer concrete compensation (money or unpaid work) or atone by showing genuine feelings of guilt and remorse.
• Victim’s Perspective – Restorative justice restores power to the victim. Their voice is heard in the legal process, and they feel that their feelings have been taken into account. Many who have been through the process report that it has reduced their feeling of being a ‘victim’ and helped them to feel safe again.
AO3
Restorative justice is tough both for victims and offenders. For offenders, they have to face up to the consequences of their actions, but for victims, they may be forced to relive frightening and upsetting experiences.
The UK Restorative Justice Council (2015) reported 85% satisfaction from victims who had taken part in face-to-face restorative justice meetings.
Sherman & Strang (2007) reviewed 20 studies involving 142 men convicted of violence and property offenses, who had taken part in restorative justice, only 11% reoffended, compared to 37% of a matched control group. So it does work!
Cost – Shapland (2007) concluded that every £1 spent on restorative justice would save the government £8 through reduced reoffending. However, there are costs involved in training mediators and high dropout rates from offenders unable to face their victims, so it may not always be cost-effective.
Remorse – Offenders must feel genuine remorse. Therefore, restorative justice is not suitable for all criminals or, indeed, all crimes. It only works where there is an obvious victim.
Soft Option – Public opinion may be against restorative justice, as it may be seen as ‘getting off lightly.’
Feminist critique – Women’s Aid have called for a ban on the use of restorative justice in cases of domestic abuse, as they believe it is inappropriate.
First-time offenders – Restorative justice is most effective with young, first-time offenders. It provides a short, sharp shock and forces them to face up to the consequences of their actions.
Essay Questions
Discuss the psychological effects of custodial sentencing. Refer to evidence in your answer (16 marks)
Discuss behavior modification in custody. Refer to evidence in your answer (16 marks)
Discuss the use of anger management as a treatment for offenders. Refer to evidence in your answer (16 marks)
Discuss restorative justice as a way of dealing with offenders (16 marks)

